Urticaria (Hives) Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in Surat
Posted in :
Urticaria (Hives) Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
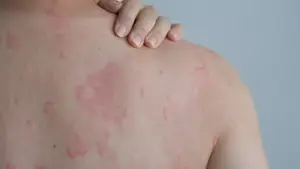
Have you ever noticed sudden red, raised, and itchy rashes on your skin? You might be suffering from Urticaria, commonly known as Hives (or “Shilas” in Gujarati).
At Allergy Cure Clinic in Surat, we see hundreds of patients struggling with these uncomfortable welts. While they affect nearly 20% of people at some point in their lives, understanding the root cause is the key to permanent relief.
In this guide, Dr. Ashish Dungarani breaks down everything you need to know about Urticaria, its triggers, and how to manage it.
What is Urticaria (Hives)?
Urticaria is a skin reaction that causes red, itchy welts that can range in size from small spots to large patches. It is not contagious, meaning you cannot catch it from (or give it to) someone else.
The Science Behind the Itch: The reaction happens when your body encounters a trigger (allergen). Your immune system releases a protein called histamine. This causes tiny blood vessels (capillaries) to leak fluid, which accumulates under the skin, creating the raised rash known as a “wheal.”
Common Causes & Triggers
Urticaria occurs when the body reacts to an allergen. However, triggers can vary hugely from person to person. Common triggers we identify at our Surat clinic include:
-
Foods: Nuts, shellfish, eggs, strawberries, wheat products, and food additives.
-
Medications: Antibiotics (like penicillin) and NSAIDs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen).
-
Environment: Extreme heat or cold, sunlight exposure, or sudden temperature changes.
-
Infections: Common colds, viral infections, or intestinal parasites.
-
Physical Triggers: Pressure on the skin (tight clothing), scratching, or insect bites.
-
Stress: High levels of stress can worsen or trigger flare-ups.
Note: In about 50% of chronic cases, the exact cause isn’t external but is related to the body’s autoimmune response.
The Two Main Types of Urticaria
Diagnosing the type of Urticaria is the first step toward treatment.
1. Acute Urticaria (Short-Term)
This lasts for less than 6 weeks. It is usually caused by a specific reaction to food, medicine, or an insect bite.
-
Diagnosis: At Allergy Cure Clinic, we can often identify the specific trigger using Skin Prick Tests or blood profiles.
-
Solution: Once the trigger is identified, avoiding it usually prevents recurrence.
2. Chronic Urticaria (Long-Term)
If the hives persist for more than 6 weeks, it is classified as Chronic Urticaria. In these cases, external allergy tests may not be enough. We may recommend further investigation to check for underlying issues, such as:
-
Thyroid function (Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism).
-
Immune system markers (ESR tests).
-
Liver function or anemia checks.
Home Remedies & Management Tips
While medical treatment is necessary for a cure, these tips can help you manage the itching and irritation at home:
-
Avoid Scratching: It makes the inflammation worse.
-
Cool Down: Use a cool compress, take a tepid oatmeal bath, or stay in a cool room. Heat worsens the histamine reaction.
-
Loose Clothing: Wear light, loose-fitting cotton clothes to avoid pressure on the skin.
-
Dietary Changes: Avoid high-histamine foods like fermented items, processed meats, chocolate, and strawberries during a flare-up.
-
Choose Mild Products: Use soaps and lotions designed for sensitive skin.
When to See a Doctor?
Home remedies can soothe the itch, but they do not cure the problem. If you have hives that last more than a few days, or if they keep coming back, you need a specialist.
Dr. Ashish Dungarani at Allergy Cure Clinic offers:
-
Advanced Allergy Testing: To pinpoint exact triggers.
-
Immunotherapy: To treat the root cause of the allergy.
-
Personalized Care: Plans tailored to your specific medical history.